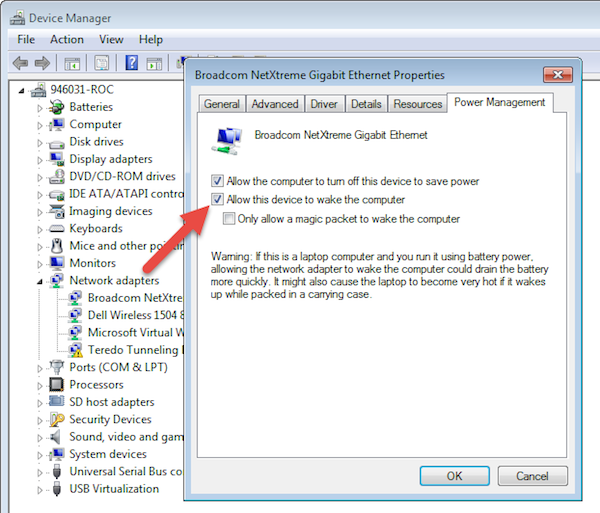
Wake For Ethernet Network Access Mac
Magic packets are usually sent over the entirety of a network and contain the subnet information, network broadcast address, and the MAC address of the target computer’s network card, whether Ethernet or wireless. With wake-on-LAN enabled, your computer will “listen” for a “magic packet” containing its MAC address while it is in sleep mode. The computer can be woken up by sending it a magic packet.
US2A1 - MAC Filtering on Ethernet PHY for Wake-On-LAN - Google Patents US2A1 - MAC Filtering on Ethernet PHY for Wake-On-LAN - Google Patents MAC Filtering on Ethernet PHY for Wake-On-LAN Info Publication number US2A1 US2A1 US13025818 US18A USA1 US 2 A1 US2 A1 US 2A1 US 13025818 US13025818 US 13025818 US 18 A US18 A US 18A US A1 US A1 US A1 Authority US Grant status Application Patent type Prior art keywords device mac address ephy block address Prior art date 2011-02-11 Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.) Granted Application number US13025818 Other versions Inventor Kenichi Suganami Current Assignee (The listed assignees may be inaccurate.
Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of the list.) Microchip Technology Inc Original Assignee Microchip Technology Inc Priority date (The priority date is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the date listed.) 2011-02-11 Filing date 2011-02-11 Publication date 2012-08-16 Links • • • • • Images • • • • • • Classifications • • G— PHYSICS • G06— COMPUTING; CALCULATING; COUNTING • G06F— ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING • G06F1/00— Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 – G06F13/00 and G06F21/00 • G06F1/26— Power supply means, e.g.
Regulation thereof • G06F1/32— Means for saving power • G06F1/3203— Power Management, i.e. Event-based initiation of power-saving mode • G06F1/3206— Monitoring a parameter, a device or an event triggering a change in power modality • G06F1/3209— Monitoring remote activity, e.g. Over telephone line, network connection • • H— ELECTRICITY • H04— ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE • H04L— TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. To improve Wake-on-LAN (WOL) functionality of a device, a Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering function may be implemented in the device's Ethernet physical layer (ePHY) block.

When the ePHY detects a WOL frame, the MAC filtering function in the ePHY may perform address comparison between the MAC address associated with the device, and the MAC address contained in the WOL frame. Performing the MAC address comparison within the ePHY allows the main system components, such as the main SOC and other components to remain in standby mode (or sleep mode) until a MAC address match has been determined. Therefore, the main system components do not need to be rebooted every time the device receives a WOL frame, only when there is a match between the MAC address of the system and the MAC address contained in the detected WOL packet. Various interface standards for connecting computers and external peripherals are in wide use today, each aiming to provide simple connectivity at high speeds. Examples of such standards include the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 1394 standard also referred to as FireWire, and the Universal Serial Bus (USB), both high-speed serial bus protocols. The most widely used networking standard for connecting computers in both Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) has been the Ethernet protocol.
If you want to attach an email to another email, there are two options you can try: Right click the email you want to attach, choose Forward As Attachment. (For contact, choose Forward as vCard) Drag the email you want to attach to the desktop directly and open a new email > Attach file > choose the email in desktop. You can also select multiple messages by holding the ‘Shift’ or ‘Ctrl’ keys when clicking, and then right-click and ‘Forward as Attachment’ as above. Outlook 2011 for Mac. Click on “E-mail” to create a new email (or attach to any reply). Select the email you want to forward in the folder, and then drag it to the body area of the email.  Locate the email you want to to attach in your inbox, or in another folder. Click the email you want to attach and hold down your mouse. Drag and drop the email into the body of your email draft. Your email should load into the email message window as an attachment. You will see it below the subject line of your email message. To confirm it attached correctly, you can double click the attachment.
Locate the email you want to to attach in your inbox, or in another folder. Click the email you want to attach and hold down your mouse. Drag and drop the email into the body of your email draft. Your email should load into the email message window as an attachment. You will see it below the subject line of your email message. To confirm it attached correctly, you can double click the attachment.
More specifically, Ethernet is the IEEE 802.3 series standard, originally based on the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) method that provided a means for two or more computer stations to share a common cabling system. CSMA/CD has formed the basis for Ethernet systems that reached transfer speeds in the megabit range, that is the Mbit/sec range. Recent switched based and/or router based Ethernet systems are capable of supporting transfer rates in the Gbit/sec range. Ethernet generally makes efficient use of shared resources, is typically easy to reconfigure and maintain, and provides compatibility across many manufacturers and systems, while keeping the cost low. The Ethernet defines a number of wiring and signaling standards for the physical layer (PHY), through means of network access at the Media Access Control (MAC)/Data Link Layer, and through a common addressing format.
Above the PHY, Ethernet enabled devices typically communicate by transmitting data packets, which comprise blocks of data that are individually sent and delivered. As with other IEEE 802 LANs, each Ethernet station is given a single 48-bit MAC address, which is used both to specify the destination and the source of each data packet. Download google drive for mac. The MAC data communication protocol sub-layer is a sub-layer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI (Open System Interconnect) model (layer 2), and acts as an interface between the Logical Link Control (LLC) sub-layer and the network's physical layer. It emulates a full-duplex logical communication channel in a multipoint network to provide addressing and channel access control mechanisms that make it possible for several terminals or network nodes to communicate within a multipoint network, typically a LAN or a WAN.